Best Describe Spontaneous and Phasic Flow in a Vien
Respiratory phasic-itywas mild inone moderate infour and marked with inspiratory flow reversal in seven83Cinterobserver agreement. Phasic blood flow C.

Doppler Ultrasound Of Normal Venous Flow
A means to measure volume increase in the lower extremities.

. Blood flow in veins should be _____ and _____ nonspontaneous and nonphasic spontaneous and nonphasic spontaneous and phasic nonspontaneous and phasic. Normal ultrasound findings include unidirectional flow compressibility of the vein and a lumen free of internal echoes Figure 1. In colour movement sonography pulsed Doppler signal is put to use to provide pictures51 Compression ultrasound is normally performed around the proximal deep veins particularly the common femoral femoral and popliteal veins.
Study Vascular Modules-Part 1 flashcards. Unidirectional flow is best demonstrated with CFDI. Superficial veins flow to the major superficial veins - Saphenous Veins.
Phasic venous flow variation with respiration is surrounded by controversy and not well understood. Sitting with legs dangling. In group 2 36 had pulsatile waveforms and 43 tricuspid regurgitation.
Deep and superficial veins of the lower extremity. Respi-ratoryphasicity dominated theflowpatternin nine Fig. PARAMETERS OF NORMAL VENOUS FLOW Venous flow.
Phasic bi-directional pulsatile Doppler signals in IVC renal and hepatic veins. Pulsatile portal venous flow occurs when there is a large difference between flow velocity at peak systole and at end diastole. Blood flow in veins should be _____ and _____ nonspontaneous and nonphasic spontaneous and nonphasic spontaneous and phasic nonspontaneous and phasic.
Sometimes a minimal physiological cyclic retrograde flow at the end of the inspiration phase is present a. Is unidirectional without retrograde flow. The current concept assigns a major role to the abdominal pump According to this model inspiratory increases in abdominal pressure compress the vena cava increasing its internal venous pressure and propelling blood upstream.
2B and affected flow equally in twowhereascardiacphasicity wasdominant inonly onesubjectCardiacphasicity was bi-phasic inseven andtriphasic inthree. An advantage of venous plethysmography is. Create flashcards for FREE and quiz yourself with an interactive flipper.
Venous flow dynamics differ in the upper and lower extremities. Spontaneous pulsatile flow D. Deep venous thrombosis DVT of the lower extremity veins is a common entity with important clinical consequences if untreated.
Before the development of sonography the clinical diagnosis of lower extremity thrombus was confirmed by venography using invasive injection of contrast material into the lower leg vein. The breathing-related intra-abdominal pressure changes lead to respiratory fluctuation of venous flow with faster flow during expiration due to lower intraabdominal pressure upward movement of diaphragm and slower flow during inspiration due to higher intraabdominal pressure downward movement of diaphragm. Characteristics of spontaneous phasic contractions of the rat portal vein.
An alteration of this flow pattern might include obstruction. Age range 21-50 years. Which of the following best describes the effects of exercise on blood flow in a non-diseased vessel.
During inspiration there is minimal flow fluctuation in the portal vein. Continuous venous flow B. Spontaneous anterograde phasic flow was present and pulsatile if flow had a cyclic retrograde compo nent.
It is very good at detecting the location of thrombus. The purposes of this study were to determine the origin and nature of normal lower limb venous Doppler flow phasicity and to assess normal and respiratory variations. Eighty-nine patients with peripheral vascular disease and 35 age-matched control subjects were studied.
The most common venous collateral pathways include the ascending lumbar presacral transpelvic and abdominal wall veins. Supine with head elevated B. Vian and axillary veins.
Mean 29 years were evaluated by detailed spectral Doppler examinations. The Doppler waveform is anterograde usually phasic and spontaneous well modulated by breathing. Vein is compressible C.
Transverse color Doppler US image shows intrahe-patic portal vein branches white containing blue signal adjacent to hepatic artery branches black containing red signal. The popliteal vein diameter and flow velocity were measured at rest by means of color duplex. Greater Lessor Small Perforators.
5 Opposite flow directions in the portal vein and adjacent hepatic artery in a pa-tient with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Minimally phasic continuous Doppler signals in portal splenic and mesenteric veins. The pulsed Doppler spectral waveform in a normal lower limb vein exhibits spontaneous and respiro- phasic flow pattern Figure 2.
Some describe scanning the superficial venous system like scanning a plate of spaghetti. VENOUS FLOW SPONTANEOUS PHASIC FLOW Venous flow responds to respiration. Normal lower extremity venous sonography demonstrates spontaneous and phasic flow whereas upper extremity venous flow dynamics are pulsatile due to the proximity of the heart.
A prospective controlled study was undertaken to determine how peripheral vascular disease PVD influences flow in the deep veins of the legMethods. The common femoral veins of 12 healthy volunteers three men and nine women. As shown in Figure 1 the portal vein possessed a spontaneous phasic contractile activity at a frequency of 003006 Hz and the amplitude of the contraction was 250 - 500 mg which is consistent with previous findings Funaki Bohr 1964.
Absence of flow C. Normal venous flow Spontaneity Spontaneous flow without augmentation Phasicity Flow changes with respiration Compression Transverse plane Augmentation Compression distal to site of examination Patency below site of examination Valsalva Deep breath strain while holding breath Patency of abdominal pelvic veins. In duplex ultrasonography blood flow in ordinary vein is spontaneous phasic with respiration and may be augmented by guide stress.
MRI in particular is highly useful in assessing the haemodynamic significance of venous compression as it has the ability to demonstrate retrograde flow in the ipsilateral iliac vein and in the collateral veins Figure 7. Requires little assistance from the patient. Thick skin allows for adequate penetration of infrared light.
In order to demonstrate the compressibility of a normal vein minimal external compression is needed with the transducer in the transverse position Figure 2. Supine with legs externally rotated D. Spontaneous phasic flow C.
Therefore the word pulsatile is reserved for describing pathologic flow in portal veins. Normal vein Doppler waveform. Flow is variable in the hepatic vein.
When performing venous sonography of a unilateral upper extremity examination. Spontaneous pulsatile flow Patient positioning for a venous PPG refill study should be. Spontaneous non-phasic flow B.
As mentioned earlier the normal portal venous waveform is described as phasic. In group 1 21 had pulsatile waveforms whereas 24 had cardiac decompensation.
Role Of Duplex Ultrasound Investigation In The Management Of Postthrombotic Syndrome Servier Phlebolymphologyservier Phlebolymphology

Venous Doppler Sonography Of The Extremities A Window To Pathology Of The Thorax Abdomen And Pelvis Semantic Scholar

Doppler Ultrasound Of Normal Venous Flow

An Example Of Normal Respiratory Phasicity Of Venous Fl Ow As The Download Scientific Diagram

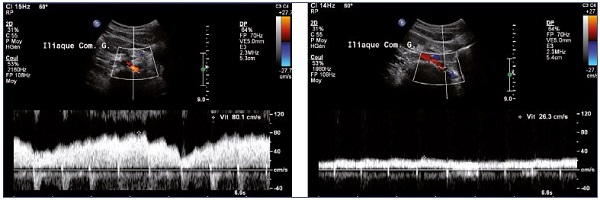
Spectral Doppler Waveform Analysis Of The External Iliac Vein Eiv Download Scientific Diagram

Triplex Of A Cephalic Vein With A Flow Measurement Arrow Download Scientific Diagram

Spectral Doppler Waveform Analysis Of The Lower Limb Veins Spontaneous Download Scientific Diagram
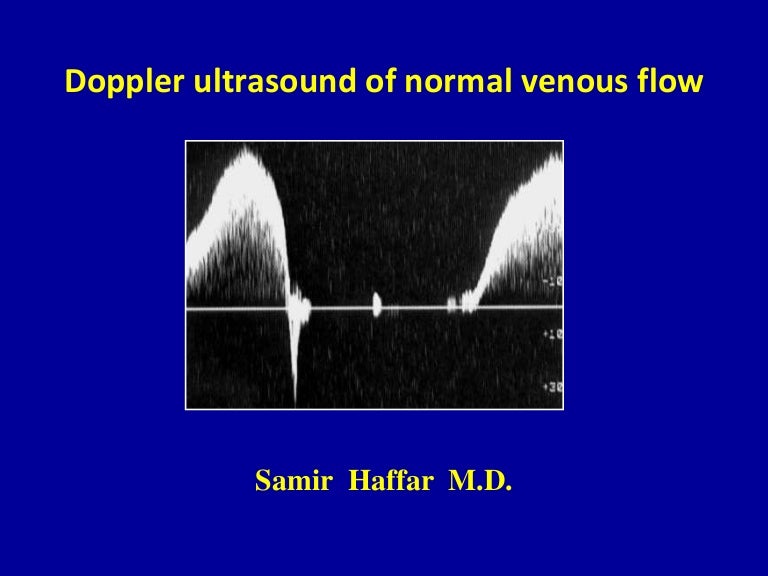
Doppler Ultrasound Of Normal Venous Flow

Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Iame

Side Difference Of The Venous Flow In The Distal Subclavian Vein In A Download Scientific Diagram

Venous Duplex Color Flow Imaging Ppt Download

Colour Flow Doppler And Pulsed Doppler Spectral Waveform At The Right Download Scientific Diagram

Venous Duplex Color Flow Imaging Ppt Download

Mechanical Function Of Internal Jugular Vein Valve Post Analysis Of M Mode Imaging Under Cardiac Monitoring Ultrasound In Medicine And Biology

Doppler Interrogation Of The Femoral Vein In The Critically Ill Patient The Fastest Potential Acoustic Window To Diagnose Right Ventricular Dysfunction Abstract Europe Pmc


